

Meter (American English spelling) or metre (British English spelling), abbreviation - m, is a unit of length in the international metric system. There are 12 in (inches) in a ft (foot) and 36 inches in one yard. A giga is thousand times of mega and a tera is a thousand times giga.An inch (abbreviation: in or ″) is a length unit in different measurement systems, including British Imperial units and US customary (Standard) units. There are various units greater than the kilo as well. The prefixes of the metric system can be remembered with the help of the mnemonic “King Henry Died of Drinking Cold Milk”. Since the year 1960s the metric system is known as the "International System of Units" or "SI" (from the French "Système International"). The metric system has its beginnings back in 1670 by a mathematician called Gabriel Mouton. Therefore, 5 km equals 5 × 1000 equals 5000 m. So, a ‘deca’ means 10 times of the base unit, ‘hecto’ is ten times of ‘deca’ or hundred times of the base unit and ‘killo’ is ten times of ‘hecto’ or thousand times of the base unit. Often when buying from an electronic components distributor or electronic components store, the markings of specifications may use different notations and it may be necessary to convert them. As we move to the left side, each unit is 10 times greater than the unit to its right side. The capacitor conversion chart below reveals the equivalents between ♟, nF and pF in an easy to use table format. SI symbol for meter is m, and one meter is 100 centimeters or 1/1000 th (10 -3) of a kilometer. The units to the left of the base unit are larger than the base unit. One meter equals to the length of the path that a light travels in vacuum for the time of 1/299,792,458 second. One approach to determine this issue is to request the help of a math guide. They discover math table troublesome subject as a rule experiencing difficulty with issues running from insights to the metric change table. Millimeter Centimeter Decameter Feet Furlong Hectometer Inches Kilometer Meter Micrometer Miles Nanometer Yard. Undergrads keep on struggling with their metric conversion chart template (Excel, Word, PDF). Millimeter Centimeter Decameter Feet Furlong Hectometer Inches Kilometer Meter Micrometer Miles Nanometer Yard. So, the word ‘deci’ means one-tenth of the base unit, ‘centi’ is one-tenth of ‘deci’ or one-hundredth of the base unit and ‘milli’ is one-tenth of ‘centi’ or one-thousandth of the base unit. Please select the length units to start metric conversion.

As we move to the right, each unit is ten times smaller or one-tenth of the unit to its left. Conversion Chart for Inches, Yardage, and Meters INCHES YARDS YARDS METERS (fractions) (decimals) 4Zx' Z, yard.125 yard.114 meters 9' Zv yard.25 yard.229 meters 13Zx' C, yard.375 yard.343 meters 18' Zx yard.5 yard.457 meters 22Zx' B, yard.625 yard.572 meters 27' Cv yard.75 yard.686 meters 31Zx' M, yard.875 yard. The length in meters is equal to the kilometers multiplied by 1,000. Since one kilometer is equal to 1,000 meters, you can use this simple formula to convert: meters kilometers × 1,000. CONVERSION TABLE FOR METRIC UNITS OF LENGTH 1 centimeter (cm) 0.01 m 1 meter 100 centimeters 1 millimeter (mm) 0.001 m 1 meter 1000 millimeters 1 millimeter (mm) 0.1 cm 1 centimeter 10 millimeters 1 micrometer (m) 0. A1C level chart in this article shows the relationship between A1C and its average blood sugar equivalent, based on the DCCT A1C conversion formula. Because this formula derived from such a group. The units to the right of the base are lesser than the base unit. For conversion from inch-pound units to SI units, multiply by the factor given in Section 5. To convert a kilometer measurement to a meter measurement, multiply the length by the conversion ratio. The following charts and tables convert surface finish or roughness between selected industry standard units. DCCT A1C conversion formula seems to work best in people with high blood sugars. The given diagram above shows the arrangement of metric units, which are smaller or bigger than the base unit. To measure larger or smaller quantities, we use units derived from the metric units.
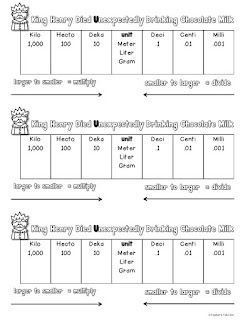

The metric system can be defined as a system of measurement that uses the litre, metre, and gram as base units of metric length (distance), capacity (volume), and weight (mass) respectively.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
